- The AI Trust Letter
- Posts
- The impact of unsafe AI
The impact of unsafe AI
Top AI and Cybersecurity news you should check out today

Welcome Back to The AI Trust Letter
Once a week, we distill the most critical AI & cybersecurity stories for builders, strategists, and researchers. Let’s dive in!
🏨 AI and Cybersecurity in the Health Sector
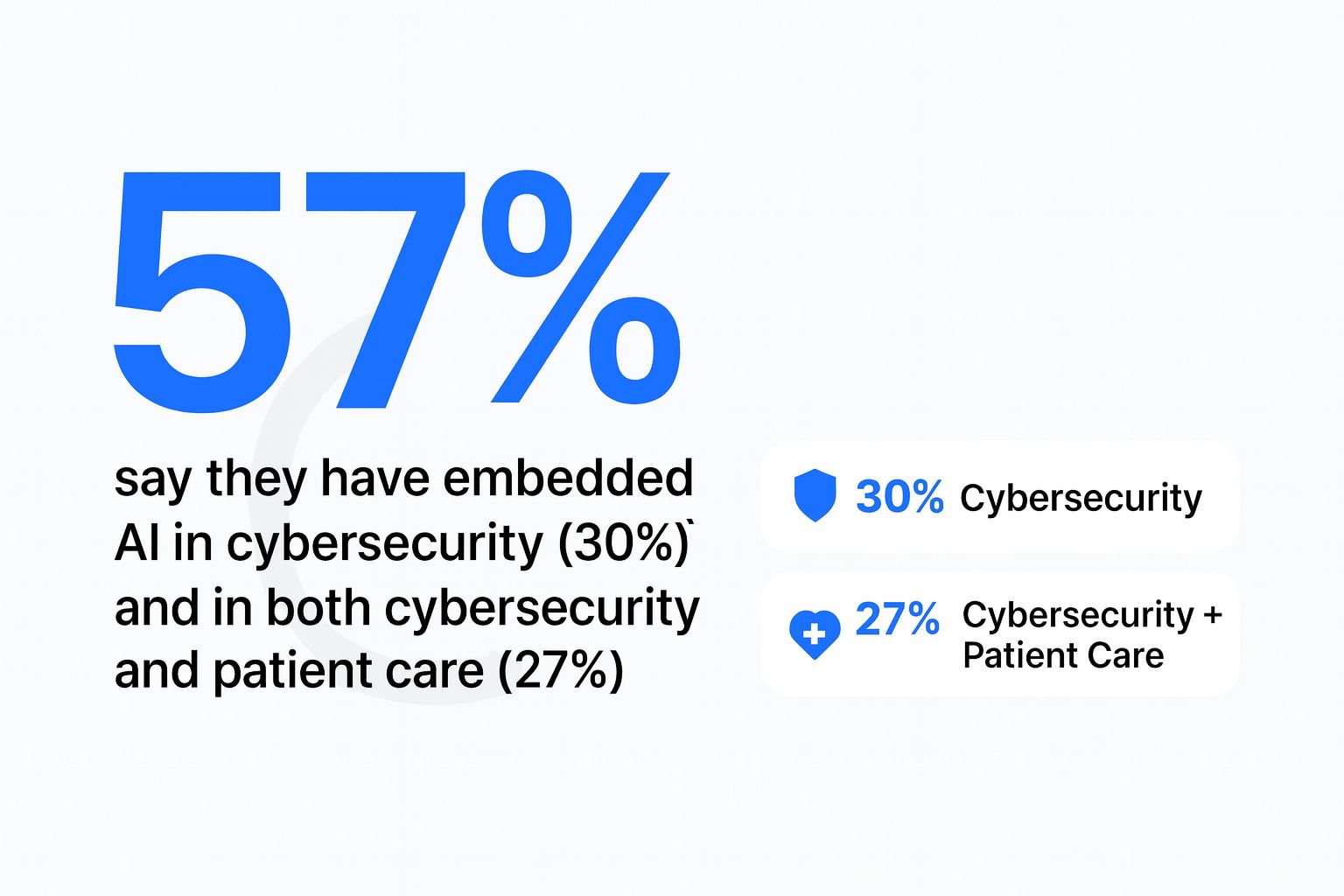
The Story:
A new study found that 93% of U.S. healthcare organizations suffered at least one cyberattack in the past year, with 72% reporting direct disruptions to patient care. These incidents ranged from ransomware and supply chain intrusions to cloud account takeovers, revealing how digital risk is now intertwined with clinical safety.
The details:
On average, each healthcare organization faced 43 attacks last year, most commonly targeting cloud collaboration tools and vendor systems.
Supply chain and ransomware incidents caused the most severe outcomes—delayed treatments, longer hospital stays, and even higher patient mortality.
The financial toll remains high: $3.9 million for the most damaging incident, largely from operational downtime and remediation costs.
Human error still drives many breaches, including misdirected patient data and weak security practices.
As more hospitals adopt AI and cloud tools, the complexity of defending clinical systems continues to grow.
Why it matters:
These findings confirm that cybersecurity failures in healthcare are not just IT problems, they are patient safety issues. Protecting care delivery now requires the same rigor as protecting data: continuous monitoring, strong vendor oversight, and staff training that connects digital hygiene with clinical responsibility.
🚨 GitHub Copilot Chat Vulnerability

The Story:
A newly disclosed flaw in GitHub Copilot Chat allowed attackers to access private repository data and manipulate AI-generated code suggestions. The vulnerability stemmed from a remote prompt injection combined with a content security policy (CSP) bypass that could exfiltrate data through disguised URLs.
The details:
Attackers could craft malicious prompts that made Copilot encode repository content into URLs, sending sensitive data back to an external server once clicked.
The issue also enabled altered AI suggestions, potentially introducing malicious code into projects.
Despite GitHub’s strict CSP rules, the attacker used a dictionary of encoded characters to circumvent restrictions.
GitHub has now disabled the Camo URL feature used for this exfiltration vector and patched the vulnerability.
Why it matters:
The incident shows how prompt injection can extend beyond text manipulation to code compromise. AI coding assistants rely on deep integration with developer environments, which increases the blast radius of security gaps. Teams using AI-assisted development should isolate repository access, audit model outputs, and restrict link-based actions to trusted sources.
🤖 Google brings AI Agents to every desk

The Story:
Google is rolling out Gemini for Enterprise, positioning its AI agent as a core productivity layer across Gmail, Docs, Sheets, and other Workspace apps. The goal is to embed AI assistants directly into daily workflows, making them accessible from any desk within an organization.
The details:
Gemini Enterprise integrates tightly with Google Workspace, enabling agents that can summarize emails, analyze spreadsheets, generate documents, and coordinate scheduling.
It also supports cross-application context, meaning an AI agent can retrieve relevant insights from Docs, Sheets, or Gmail in a single query.
Google says the system maintains enterprise-grade security and compliance, with admin-level controls for data access and model interactions.
Rollouts begin with enterprise customers, with plans to extend to smaller organizations in early 2026.
Why it matters:
This shift marks Google’s move to standardize AI assistance as part of core office infrastructure rather than an add-on tool. As enterprises adopt agentic workflows, governance and auditability will become key, especially as these agents handle sensitive business data and decision-making at scale.
📢 AI vs Human Voice: Can you tell the difference?

The Story:
A new study from the University of Zurich found that most people struggle to distinguish between AI-generated and real human voices. The research, which involved more than 5,000 participants across 10 countries, highlights how natural synthetic voices have become and how unprepared the public may be for potential misuse.
The details:
Participants listened to clips generated by systems like OpenAI’s Voice Engine, ElevenLabs, and Microsoft’s Azure Speech alongside human recordings.
Accuracy rates in identifying synthetic voices averaged below 60%, meaning people guessed wrong nearly half the time.
English and German speakers performed slightly better than those in other languages, but only by a small margin.
Even when informed that some voices were AI-generated, listeners often relied on tone or emotion, both of which current voice models now mimic convincingly.
Why it matters:
Voice cloning has rapidly advanced, enabling lifelike impersonations for entertainment and accessibility, but also for scams and disinformation. As AI voice synthesis spreads into customer support, media, and personal assistants, stronger watermarking, verification, and consent systems are becoming essential to prevent misuse and rebuild public trust.
🏦 Financial Authorities Warn About Risks of AI

The Story:
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) have both issued reports urging regulators to closely monitor the growing use of artificial intelligence in the financial sector. They warn that unchecked adoption could introduce systemic risks if a few large AI vendors dominate critical infrastructure and decision-making systems.
The details:
The FSB found that banks and financial institutions are becoming increasingly dependent on a small group of providers for cloud, hardware, and large language models, creating potential concentration risk.
Additional concerns include model governance, cyber resilience, and the amplification of market volatility through automated decision systems.
The BIS report notes that while AI can improve central bank operations and regulatory efficiency, it also demands new expertise in governance, data integrity, and human oversight.
Both organizations call for coordinated international standards to address data gaps, align taxonomies, and enhance transparency around AI usage in finance.
Why it matters:
AI is already reshaping financial services, from fraud detection to algorithmic trading, but its rapid integration brings new dependencies and vulnerabilities. Regulators are signaling that resilience and accountability must evolve alongside innovation, ensuring that the technology strengthens rather than destabilizes financial systems.
What´s next?
Thanks for reading! If this brought you value, share it with a colleague or post it to your feed. For more curated insight into the world of AI and security, stay connected.
