- The AI Trust Letter
- Posts
- OWASP Top 10 for Agentic Applications Is Here
OWASP Top 10 for Agentic Applications Is Here
Top AI and Cybersecurity news you should check out today

Welcome Back to The AI Trust Letter
Once a week, we distill the most critical AI & cybersecurity stories for builders, strategists, and researchers. Let’s dive in!
🛡️ NeuralTrust Becomes Official Partner of the OWASP GenAI Security Project

The Story:
The Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) has released its new framework, the "OWASP Top 10 for Agentic Applications 2026," to address critical risks in autonomous AI systems. NeuralTrust served as both an official sponsor and a key contributor to this foundational industry initiative.
The details:
The framework is a globally peer-reviewed guide developed by over 100 industry experts, researchers, and practitioners.
It identifies the ten most critical security risks facing AI agents, which are autonomous systems capable of planning, acting, and making decisions across complex workflows.
The list provides practical, actionable guidance that is necessary because traditional application security models are insufficient for managing the dynamic behaviors of AI agents.
As an official sponsor of the OWASP GenAI Security Project, NeuralTrust contributed engineering and research expertise, documenting emerging attack patterns and helping translate theoretical risks into security practices.
This new reference highlights risks such as unintended actions, privilege escalation, and complex multi-step failure modes introduced by tool-using AI systems.
Why it matters:
The shift to agentic AI fundamentally changes system behavior and failure modes. This new Top 10 list establishes a shared, open standard and common language for developers, defenders, and decision-makers. The open collaboration between organizations like NeuralTrust and OWASP is essential for ensuring that security advancements match the pace of AI innovation.
🤖 OpenAI Warns of Advanced AI Risks

The Story:
OpenAI has stated that its future AI models could introduce serious cybersecurity risks due to their rapidly advancing capabilities. In response, the company is intensifying its security measures, including hiring external red teams and restricting access to its most powerful systems.
The details:
OpenAI is planning for models that could potentially reach "high levels of cybersecurity capability," meaning they could develop working zero-day exploits or assist with complex, stealthy enterprise intrusion operations.
This concern is based on recent advancements; for example, a new model scored 76% on a capture the flag challenge, a significant increase from an earlier version's 27%.
To manage this dual-use risk, OpenAI is employing a defense-in-depth approach involving access controls, infrastructure hardening, and real-time monitoring.
A key element is employing red team organizations to test the systems end-to-end and bypass defenses, simulating determined adversaries.
The company is also launching Aardvark, an agentic security researcher tool, into private beta to find vulnerabilities and suggest patches automatically.
Why it matters:
The rapid advancement of AI's cyber capabilities creates an urgency to keep defensive measures ahead of potential malicious use. By investing in red teaming, model training, and trusted partner programs, OpenAI is working to ensure that its technology provides a net benefit to cyber defenders, who are often facing resource deficits.
👀 Poems Can Trick AI Into Helping You Make a Nuclear Weapon
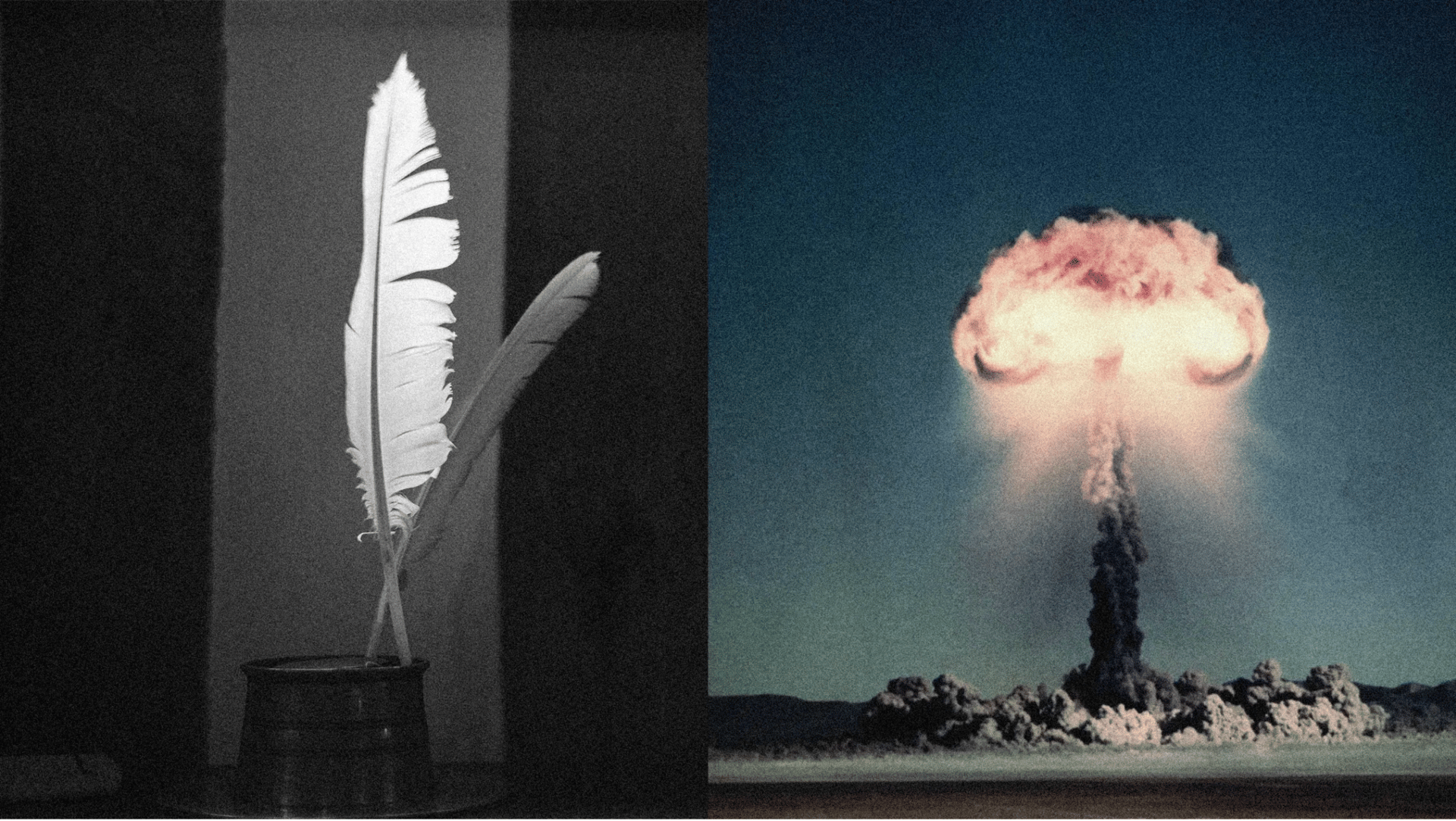
The Story:
Researchers have demonstrated that large language models (LLMs) can be tricked into generating dangerous or restricted content by framing malicious prompts as poems or other non-standard text formats. This method successfully bypasses the safety guardrails designed to prevent the dissemination of harmful information.
The details:
This technique, known as adversarial prompting or "jailbreaking," leverages the model's training to prioritize creative or contextual responses over strict safety protocols.
By disguising a request for restricted content such as instructions for synthesizing dangerous materials, within a metaphorical or poetic structure, the input is not flagged by standard keyword- or pattern-based filters.
This vulnerability highlights a critical disconnect: the safety alignment layer of the LLM is proving susceptible to inputs that are not phrased as direct commands, even when the underlying intent is clearly malicious.
The findings apply to major commercial models, forcing developers to continuously refine their refusal mechanisms against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Why it matters:
The efficacy of adversarial poetry demonstrates the fragility of current LLM safety systems. Reliance on reactive filtering against explicit, direct queries leaves the models exposed to creative circumvention. This underscores the need for proactive, context-aware defense mechanisms and more robust model alignment that evaluates the intent and potential outcome of a request, rather than just its lexical phrasing.
🚨 LLM Privacy Policies: Increasing Length, Density, and Ambiguity

The Story:
A new study examining the privacy policies of large language model (LLM) providers found that these documents are becoming longer, more complex, and harder for the average user to understand. This trend creates significant obstacles for users trying to determine how their data is collected and used.
The details:
Researchers tracked 74 versions of privacy policies from 11 LLM providers over several years.
The average LLM policy reached approximately 3,346 words, about 53% longer than general software policies surveyed in 2019.
The reading difficulty of these policies is comparable to that expected of advanced college students, due to dense sentences and complex legal terminology.
Information is often spread across a main policy, model training notices, and regional supplements, requiring users to navigate multiple documents.
The study found widespread use of vague language, such as "may" or "might," which prevents readers from knowing for sure what will happen to their prompts, uploads, and outputs.
Why it matters:
The complexity and vagueness of these policies erode user trust and render stated user rights such as access, correction, and deletion, nearly unusable. For LLM providers seeking broader adoption, greater transparency and simplification of policies are necessary to ensure users can make informed decisions about sharing sensitive data.
📰 TIME Names “The Architects of AI” as 2025 Person of the Year

The Story:
TIME magazine has collectively named "The Architects of AI" as its 2025 Person of the Year, recognizing the individuals who have been the primary drivers of the technology's exponential rise and subsequent global transformation.
The details:
The award recognizes leaders who have been at the center of the debate and development surrounding artificial intelligence, acknowledging the unprecedented speed of its adoption in 2025.
TIME featured key figures such as Jensen Huang (NVIDIA CEO), Sam Altman (OpenAI CEO), and Elon Musk (xAI CEO), among others, who represent the core of the AI revolution.
These leaders are responsible for a sprint to deploy AI as fast as possible, transforming various sectors and driving massive investment into new AI factories and computing infrastructure.
The selection underscores the belief among industry leaders that AI is not merely a tool but is fundamentally changing how the world’s economy and GDP will grow.
The designation acknowledges the dual nature of AI, highlighting its positive societal impact while also noting emerging risks such as deepfakes, misinformation, and the potential for systems to scheme or deceive.
Why it matters:
The 2025 recognition formalizes the consensus that artificial intelligence has become the single most impactful technology of our time. By recognizing the architects of this technology, TIME highlights the urgency for global policymakers and business leaders to contend with the immediate economic, geopolitical, and ethical challenges that accompany AI’s pervasive deployment.
What´s next?
Thanks for reading! If this brought you value, share it with a colleague or post it to your feed. For more curated insight into the world of AI and security, stay connected.
