- The AI Trust Letter
- Posts
- 2026: The year of Agentic AI
2026: The year of Agentic AI
Top AI and Cybersecurity news you should check out today

Welcome Back to The AI Trust Letter
Once a week, we distill the most critical AI & cybersecurity stories for builders, strategists, and researchers. Let’s dive in!
🛡️ Gartner Predicts 2026 Will Be The Year of AI Agent Security
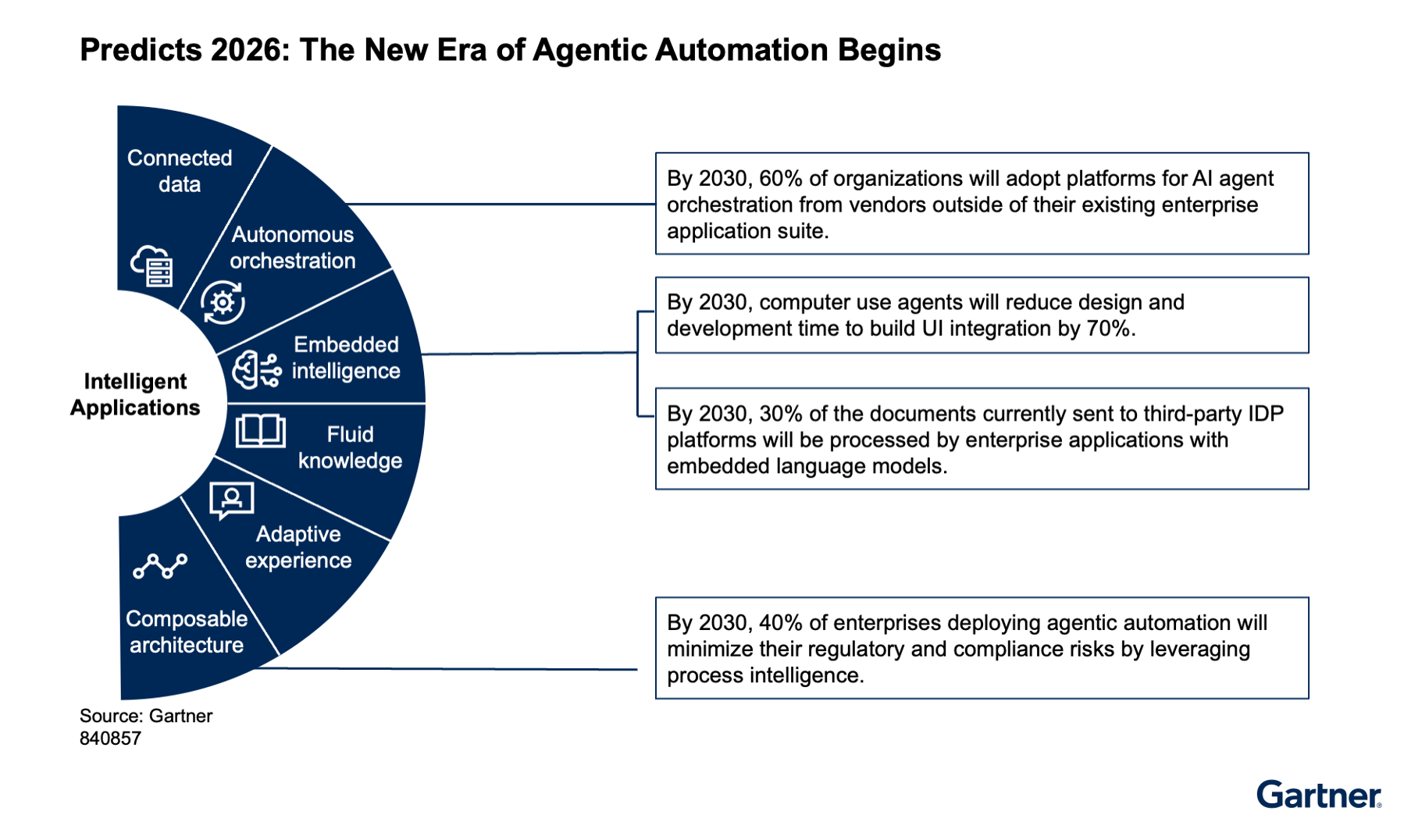
The Story:
Gartner reports that the focus of enterprise AI is shifting from simple chatbots to autonomous agents embedded in software. This rapid adoption is leading to "ungoverned sprawl," where security teams struggle to track or secure these tools. Without proper oversight, organizations face rising technical debt and increased vulnerability to data abuse.
The details:
By 2030, an estimated 33% of IT work will be dedicated to remediating "AI data debt" to secure unstructured internal data.
Organizations that bypass offensive testing before deployment are projected to face twice as many security incidents by 2028 compared to those that prioritize preproduction checks.
By 2029, a lack of "AI explainability" in vendor tools is expected to delay 50% of critical cybersecurity deployments due to noncompliance with global regulations.
Many cybersecurity leaders lack the tools to discover unsanctioned AI agents, leading to ineffective access controls across internal and cloud storage.
Why it matters:
The rush to deploy AI often ignores the foundational security required for autonomous systems. To mitigate these risks, companies should treat AI agents as distinct identities with granular access permissions. Integrating security teams early in the development process prevents the accumulation of "cybersecurity debt" that becomes more expensive and difficult to fix after a product is live.
🤖 OpenAI Launches GPT-5.2 Codex for Agentic Engineering

The Story:
OpenAI released GPT-5.2 Codex, a model optimized for long-horizon software engineering and defensive cybersecurity. Unlike earlier autocomplete tools, this version manages complex tasks across entire repositories and handles multi-step workflows.
The details:
Native compaction allows the model to maintain state during extended coding sessions, which supports large-scale refactors and framework migrations.
The model reached 56.4% accuracy on SWE-Bench Pro, showing an improved ability to generate correct patches within large, unfamiliar codebases.
New features assist with vulnerability research, fuzzing, and attack surface analysis, supported by a trusted access pilot for security professionals.
Enhanced vision performance enables the interpretation of technical diagrams and UI screenshots to help translate design mockups into functional code.
Why it matters:
The update transitions AI from a coding assistant to an autonomous agent capable of executing end-to-end workflows. By addressing long-context retention and cybersecurity research, OpenAI provides a tool for developers to handle architectural changes and security audits with less manual intervention.
💡 OWASP Top 10 Security Risks for Agentic Applications Explained

The Story:
The OWASP Gen AI Security Project published the Agentic Security Initiative (ASI) Top 10 for 2026. This framework addresses the unique risks posed by autonomous AI agents, which differ from traditional LLM vulnerabilities because of their ability to plan and execute multi-step tasks independently.
The details:
Attackers can redirect an agent's core objectives or persistently corrupt its long-term memory to influence future decisions.
Agents granted too much autonomy may use legitimate tools in unintended ways, leading to unauthorized actions or resource exhaustion.
Autonomous systems represent a new class of non-human identities that require zero-trust management to prevent privilege escalation.
Vulnerabilities can arise from compromised third-party APIs or insecure communication protocols between different AI agents.
Attackers may exploit the perceived authority of an agent to deceive human users into bypassing security controls.
Why it matters:
The shift from static chatbots to autonomous agents increases the attack surface significantly. Traditional security models are insufficient for systems that can chain actions across different environments. Organizations must adopt "Least-Agency" principles and robust observability to monitor agent behavior and prevent cascading failures.
🚨 Hacks, Thefts, and Disruption: The Worst Data Breaches of 2025

The Story:
TechCrunch reports that 2025 was the most damaging year on record for cybersecurity, characterized by a shift from simple data theft to systemic economic and operational disruption. State-linked actors and ransomware groups targeted critical infrastructure, government agencies, and global supply chains with unprecedented scale.
The details:
State-sponsored hackers breached the U.S. Treasury, multiple federal agencies, and systems linked to nuclear security, while Russian-linked groups compromised sealed records in the U.S. court system.
The Clop ransomware group exploited a previously unknown vulnerability in Oracle’s E-Business Suite, leading to the mass extortion of dozens of major corporations and the theft of sensitive executive data.
A major hack at Jaguar Land Rover halted production for months, causing a multi-billion pound economic ripple and triggering a £1.5 billion government-backed support package in the UK.
Credit reporting firm 700Credit saw the exposure of 5.6 million personal records, while South Korean e-commerce giant Coupang suffered a prolonged breach impacting tens of millions of customers.
Why it matters:
The incidents of 2025 demonstrate that detection capabilities and supply-chain dependencies remain critical weaknesses. Cybersecurity is no longer just about protecting privacy; it is now a matter of national economic stability and the continuity of physical production and essential services.
🤝 NeuralTrust and UPF Partner for Responsible AI Research

The Story:
NeuralTrust is collaborating with researchers from Pompeu Fabra University to develop tools for ethical and inclusive AI. This partnership focuses on creating technical standards for fairness and transparency in large language models and autonomous agents.
The details:
Key Research Areas: The project focuses on automated bias detection, misinformation mitigation, and accessibility frameworks for users with cognitive differences.
Funding and Collaboration: Supported by the Spanish State Research Agency, the initiative involves experts in social computing and natural language processing to bridge academic research and industrial application.
Bias Mitigation: Researchers aim to reduce harmful outputs, noting that current studies show a significant percentage of model responses in specialized fields contain racial bias or fabricated information.
Governance and Compliance: The collaboration aligns with the EU AI Act and works with the Spanish Agency for AI Supervision to help organizations manage risks and meet legal requirements.
Why it matters:
The transition to autonomous AI requires technical guardrails to prevent discrimination and errors. By combining academic research with industrial security platforms, this project provides the tools necessary to deploy reliable AI systems that comply with emerging international regulations.
What´s next?
Thanks for reading! If this brought you value, share it with a colleague or post it to your feed. For more curated insight into the world of AI and security, stay connected.
